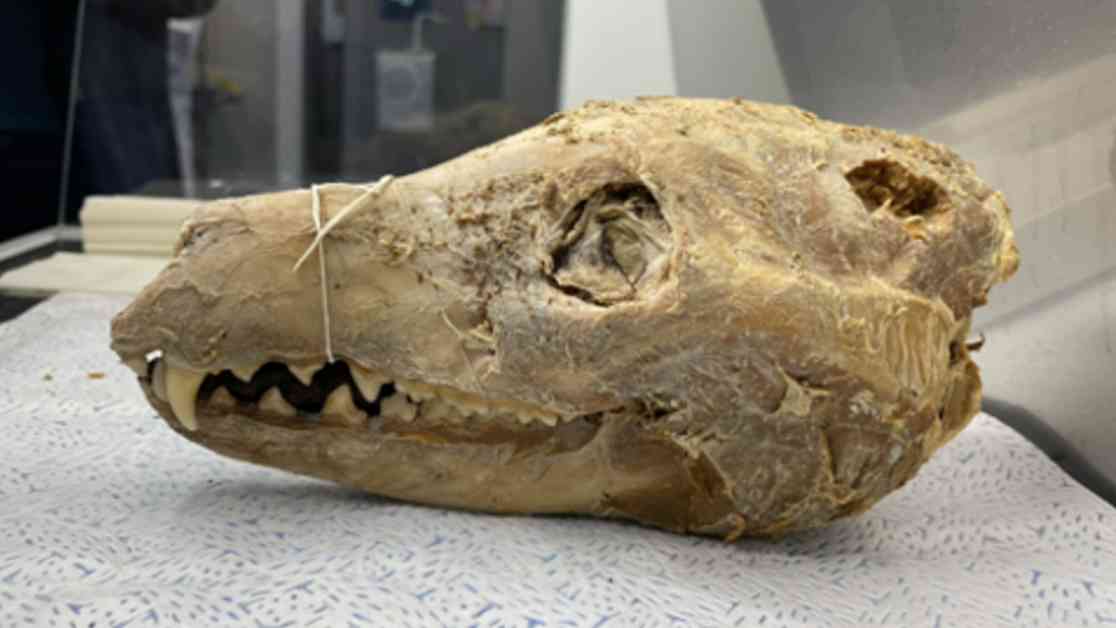
Scientists have successfully reconstructed the most complete Tasmanian tiger genome from a 110-year-old pickled head, offering hope for the potential resurrection of the extinct species. This groundbreaking achievement, led by Colossal Biosciences, involved analyzing the DNA and RNA from the well-preserved specimen to gain insights into the genetic makeup and biological functions of the iconic marsupial.
Andrew Pask, a genetics and developmental biology professor at the University of Melbourne, expressed astonishment at the level of detail they were able to extract from the historic sample. The Tasmanian tigers, also known as thylacines, were key predators in their ecosystem before their extinction in 1936 due to human activities. With the complete genome now available, there is a possibility of reintroducing the species back into the wild.
The genome, comparable in size to a human genome, consists of 3 billion nucleotides, with some gaps that researchers aim to fill through further sequencing efforts. Additionally, the discovery of RNA fragments in the pickled head provides valuable information on the thylacine’s sensory abilities and brain functions while alive. This unprecedented insight into the biology of the species opens up new avenues for understanding its behavior and ecology.
In a related development, Colossal Biosciences has made progress in assisted reproductive technologies for marsupials, such as the fat-tailed dunnart, a close relative of the Tasmanian tiger. By inducing ovulation in dunnarts and using them as surrogates for thylacine embryos, the company is advancing towards creating a living thylacine through innovative reproductive methods. The team is also pioneering the development of an artificial uterus device to support the growth of marsupial embryos, marking a significant step forward in conservation and genetic engineering efforts.
These breakthroughs not only hold promise for the de-extinction of the Tasmanian tiger but also have broader implications for endangered marsupial species and captive breeding programs. The meticulous research and technological advancements spearheaded by Colossal Biosciences are reshaping our understanding of extinct species and offering new possibilities for conservation and genetic restoration in the modern world.