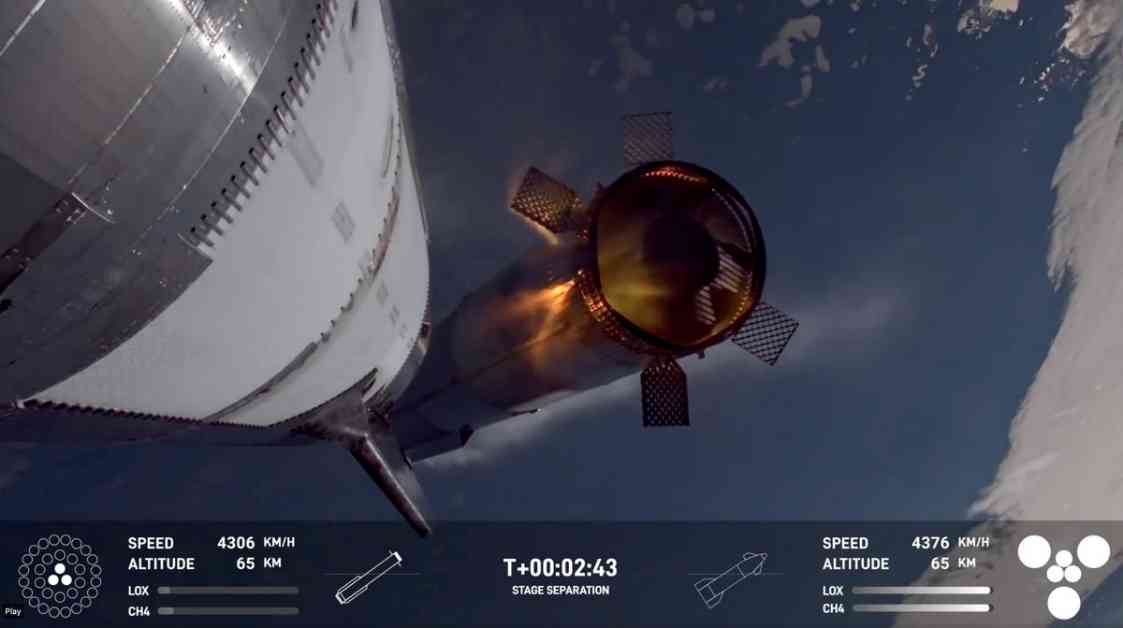
SpaceX Starship Explosion: Elon Musk Attributes Cause to Propellant Leak
In a dramatic turn of events, the seventh test flight of SpaceX’s Starship on January 16, 2025, ended with a successful landing of the rocket’s first stage but also the loss of the Starship vehicle’s upper stage. The two stages of the Starship megarocket separated during the test flight, with the upper stage being lost about six minutes later at SpaceX’s Starbase site in South Texas.
Elon Musk’s Explanation
SpaceX’s founder and CEO, Elon Musk, attributed the explosion that destroyed the upper stage of the Starship vehicle to a propellant leak. Musk revealed that the preliminary indication pointed towards an oxygen/fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall, which built pressure in excess of the vent capacity. This pressure overload led to a fire in the aft section of the ship, resulting in a rapid unscheduled disassembly, a term used for a spacecraft explosion.
Next Steps and Future Plans
Despite the setback, SpaceX plans to continue flying the Starship often in 2025, with the company applying for permission to launch the megarocket up to 25 times this year. Musk emphasized the importance of conducting a thorough investigation in coordination with the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration to implement corrective actions and improvements for future Starship flight tests.
Impact Beyond SpaceX
The anomaly during the flight test had effects beyond the SpaceX sphere, with the FAA briefly slowing and diverting aircraft around the area where space vehicle debris was falling. However, normal aircraft operations resumed shortly thereafter, ensuring the safety of the public on the ground, water, and in the air.
The incident serves as a reminder of the risks and challenges associated with space exploration and the continuous efforts needed to improve safety measures. As SpaceX and other space agencies push the boundaries of space travel, incidents like these highlight the importance of thorough investigations, transparency, and collaboration to ensure the future success and safety of space missions.