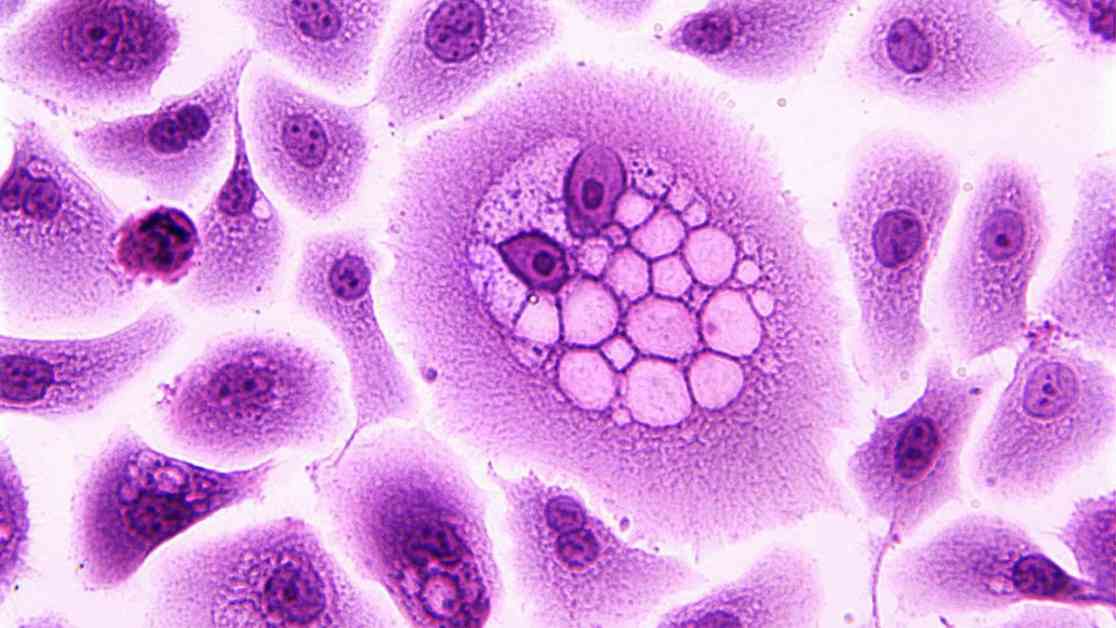
Viruses are not just the common cold or flu; some viruses can actually lead to cancer. While smoking, exposure to toxins, and genetic mutations are well-known causes of cancer, viruses can also play a role in the development of the disease. There are at least seven viruses that have been identified as contributors to cancer in humans, either directly or indirectly.
One of the most well-known cancer-causing viruses is human papillomavirus (HPV), which is responsible for more than 37,000 new cancer cases in the U.S. each year. HPV is associated with cervical cancer, as well as anal, oropharyngeal, penile, vaginal, and vulvar cancers. The virus transforms healthy cells into abnormal, tumorous cells by producing proteins that deactivate the body’s natural tumor suppressor systems.
Other viruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human T-cell lymphotropic virus, cause cancer through different cellular and genetic mechanisms. These viruses lead to the aggressive replication of cancerous cells that evade the body’s defense systems. Factors like specific virus strains, weakened immune systems, and exposure to environmental carcinogens can influence whether infection with these viruses leads to cancer.
Additionally, viruses like hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) can indirectly cause cancer by infecting the liver and causing inflammation and scarring. Chronic infections with HBV or HCV can lead to long-term liver damage, increasing the risk of liver cancer. HIV can also raise the risk of cancer by causing chronic inflammation and weakening the immune system, making the body more susceptible to other cancer-causing viruses.
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of virus-related cancers. Vaccines are available for HPV and HBV and have been shown to be highly effective in preventing infections. Using condoms, not sharing needles, and taking preventative medicines like PrEP can reduce the risk of contracting HIV. Antiviral treatments can also help manage conditions like HIV and HBV, reducing the likelihood of cancer development.
Overall, understanding how viruses can lead to cancer and taking steps to prevent and treat these infections can help decrease the global cancer burden. It’s important to stay informed about the risks associated with these viruses and take proactive measures to protect your health.